Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
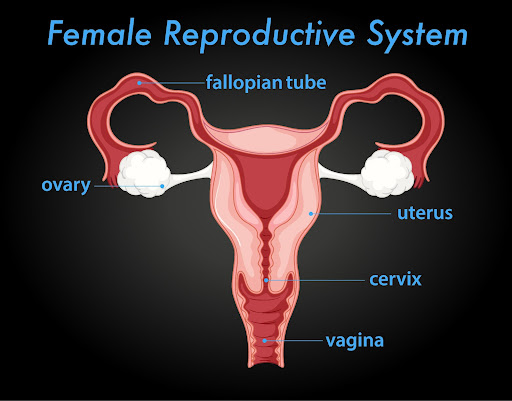
Women usually have two ovaries that produce ova or eggs. They create the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. Ovaries are walnut- sized organs, located on either side of the uterus, in the lower abdominal area. When a woman gets pregnant, the ovaries create eggs that move through the fallopian tubes to the uterus. If the sperm fertilizes an egg it could settle in the uterus lining and result in pregnancy.
What is an ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer happens when abnormal cells in your ovaries or fallopian tubes multiplies and get out of control forming a tumor. Ovarian cancer can spread to the other parts of the body if it is not treated timely. It is called metastatic ovarian cancer. Ovarian cancer spreads from pelvis to the lymph nodes, abdomen, intestines, stomach, chest or liver.
Ovarian cancer has significant signs, but the early symptoms are unclear and easy to ignore. Only 20% of ovarian cancers are diagnosed in the initial stage. A woman’s risk of getting ovarian cancer at some point in her life is 1 in 78. Women who are 63 or older are more likely to get ovarian cancer. Comparatively it is more commonly found in white women.
Types of ovarian cancer:
Basically, ovaries are made up of 3 types of cells and each cell can create a different type of tumor.
- Epithelial ovarian carcinomas: develop in the layer of tissue on the outer side of the ovaries. Approximately 85%-90% of the malignant ovarian cancers are epithelial ovarian tumors.
- Stromal tumors: develop in the hormone producing cells. 7% of ovarian cancers are stromal tumors.
- Germ cell tumors: occurs in egg producing cells. These tumors are rare.
Symptoms of ovarian cancer:
The initial signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer are not obvious and there is no routine diagnostic screening for ovarian cancer. Women in advance stage might experience certain symptoms.
Early symptoms:
- Abdominal pressure, bloating and pain
- Feeling of fullness after eating your meal
- Problem in eating
- Frequent urination
These early signs of ovarian cancer can be the symptoms of other harmless conditions, but in ovarian cancer these signs can last longer and will be prominent in your daily life. Consult your doctor if these symptoms occur repeatedly.
Later symptoms:
Ovarian cancer can lead to other symptoms if not detected early. Some of them are:
- Fatigue
- Indigestion
- Back ache
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Unpleasant intercourse
- Dermatomyositis
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Constipation
The symptoms will linger on if they are because of ovarian cancer and symptoms become more intense as the tumor grows. At this point the cancer spreads outside of your ovaries, making it more complex to treat.
Severe symptoms:
Some people may experience these symptoms if the cancer has reached its last stage without any obstruction:
- Fluid accumulation around the lungs resulting in shortness of breath, cough and chest pain
- Fluid buildup in the abdomen
- bowel obstruction
Post-menopausal symptoms:
Ovarian cancer symptoms are the same pre- and post- menopause, one major difference is bleeding. Because of menopause you will not have your monthly period. During menopause if you have stopped having your periods and then notice bleeding, it could be the symptom of ovarian cancer. Ovarian cancer is more likely to happen in women over 60.
Causes of ovarian cancer:
Ovarian cancer happens when cells in or around the ovaries develop mutations in their DNA. A cell’s DNA tells the cell what to do. The mutations instruct the cells to grow rapidly creating tumor. The healthy cells would perish and cancer cells will keep on growing. These cells further spread to the other parts of the body.
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is not known. But some people are at a greater risk of developing this condition. Some of the risk factors are:
- It is mostly diagnosed in older adults or women over 60 years of age.
- Obesity or being overweight
- Having a family history of ovarian cancer or gene mutation
- Never being pregnant or having children in later life increases the risk of having ovarian cancer.
- Endometriosis
- Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy.
- Age when menstruation started or ended.
Can we prevent ovarian cancer?
There is no certain way to prevent ovarian cancer but, you can lower the risk:
- Think about taking birth control pills. Consult your doctor about oral contraceptives. Birth control pills minimize the risk of cancer but these medications come along with other risks.
- Consult your doctor about your risk factors. If you have a family history of cancers; share it with your doctor. Your doctor may suggest you a gene counselor who can assist you to decide about genetic testing. You may have to remove your ovaries to prevent cancer if you have a gene change that elevate your risk of ovarian cancer.
Conclusion:
Irrespective of its type, Cancer diagnosis is alarming. If you or your dear ones are diagnosed with ovarian cancer, you may feel broken and frustrated. Your doctor can help you in this tough time. Try to get in touch with other cancer patients and join some support groups to vent out all the negative emotions.