Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
What is sickle cell disease (SCD)?
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disease that runs in your family and it is not contagious. This disorder impacts the shape of red blood cells which moves oxygen to every region of the body. Typically red blood cells are healthy, pliable and round discs that transfer smoothly through the blood vessels. In sickle cell disease or anemia some red blood cells look like sickles or crescent moons. These cells become rigid and sticky which can slow or obstruct blood flow. It is perilous and can lead to agony, anemia and other symptoms. There is no cure for people with sickle cell anemia. Certain treatments can relief some pain and stave off complications linked to this disease.
Earlier the babies with sickle cell anemia hardly survived but now because of early diagnosis and new treatments, almost half of all people with sickle cell anemia can make it to their 50s. Still people with this disorder have to face serious medical complications. Doctors have treatments that lessen the likelihood of problems and reduce the symptoms when they do occur.
Who is more affected by sickle cell anemia?

Children are at a greater danger for sickle cell disease if both the parents have sickle cell trait. Hemoglobin electrophoresis is a blood test that can identify the type you have.
Approximately 100,000 people in United States have sickle cell disease and mostly are African American. It may also trouble people that have endemic malaria and includes people of some ethnicities are the Mediterranean, African, Southern European, Middle Eastern or Asian Indian ancestry.
Types of sickle cell disease:
There are different forms of sickle cell disease. The precise type of abnormal hemoglobin you possess is one of several factors that will determine the type that you or your child receives. Hemoglobin SS also known as sickle cell anemia is the most chronic type of disorder. Other common types are:
- Hemoglobin SC
- Hemoglobin sickle beta thalassemia
Rare types are:
- Hemoglobin SD
- Hemoglobin SE
- Hemoglobin SO
Causes of sickle cell disease:
Problem in Hemoglobin-beta gene found on chromosome 11 causes sickle cell disease. This creates unhealthy hemoglobin.
People with sickle cell disease derive the disease from their biological parents. In this disorder the genes that create healthy red blood cells mutates. Children who inherit abnormal hemoglobin protein gene from both the parents have a 1 in 4 chance of inheriting this disease but when a child inherits mutated gene from one of the biological parent he has sickle cell trait. If the child is born with one abnormal hemoglobin-beta gene, they may become the conveyor of the disease. Generally carriers don’t form SCD symptoms but they can transfer the gene to their children if their partner also carries sickle cell trait.
Symptoms of sickle cell disease:
Signs and symptoms of SCD are noticeable at the age of 6 months. They differ from person to person and may change with the passage of time. Some of the symptoms are:
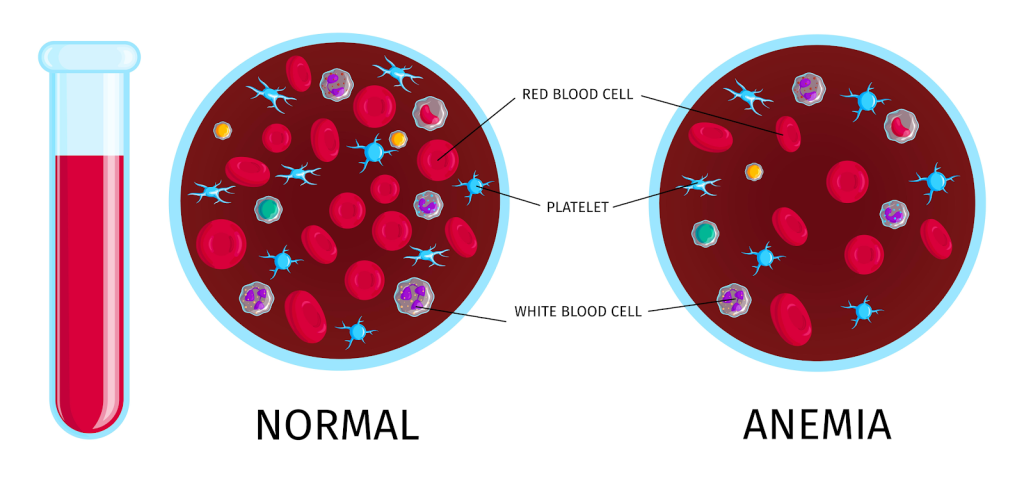
- Anemia: sickle cells easily break and perish. Generally red blood cells survive for 120 days before they are replaced but sickle cells expire in 10-20 days leading to anemia. Due to insufficient red blood cells your body fails to get ample oxygen and this makes you fatigued and worn out.
- Pain crises: recurrent episodes of pain and discomfort are called pain crises and are a prime symptom of sickle cell disease. Pain or discomfort occurs when abnormal red blood cells obstruct the blood flow via little blood vessels to your chest, abdomen and joints. The pain oscillates in intensity and continues for few hours to certain days. Some people suffer from very less pain crises in a year while others get many throughout the year. An acute pain crises needs a hospital stay. Some adults with sickle cell anemia have intense pain which is because of some bone or joint damage, ulcers or some other causes. These pain episodes are chief symptom of sickle cell disease.
- Inflammation on Hands and feet: when the unhealthy sickle shaped red blood cells obstruct the blood circulation it results in the swelling of hands and feet.
- Recurring infections: sickle cells can hurt the spleen, exposing you more to the infections. Normally infants and children get vaccinations and antibiotics to avert all possible fatal infections such as pneumonia.
- Slow growth or puberty: red blood cells supply the required oxygen and nutrients for the growth. Inadequate healthy red blood cells can impede the growth of infants and children and can hinder puberty in teenagers.
- Problems regarding Vision: tiny blood vessels that provide the eyes can be packed with sickle cells. This can detach the retina-the part of the eye that holds visual images and results in vision problems.
Some of the other symptoms are fatigue, irritability, crankiness in babies, bedwetting, jaundice, hands and feet inflammation, persistent infections and pain in legs, chest, back and arms.
Conclusion:
Families and medical professionals have battled the tragic effects of babies born with sickle cell anemia for more than a century. Few newborns survived to reach their fifth birthday. Healthcare professionals made significant advancements in treating sickle cell anemia starting roughly ten years ago.
A newborn today will probably live well into their 50s. Research has made it possible for medical professionals to manage sickle cell anemia as a chronic condition. However, it is a disease with significant, and occasionally life-threatening, medical implications. If you or your child has sickle cell anemia, you could be appreciative of the previous developments while also looking forward to the future. The treatment of sickle cell anemia is the primary focus of scientists and medical professionals.