Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
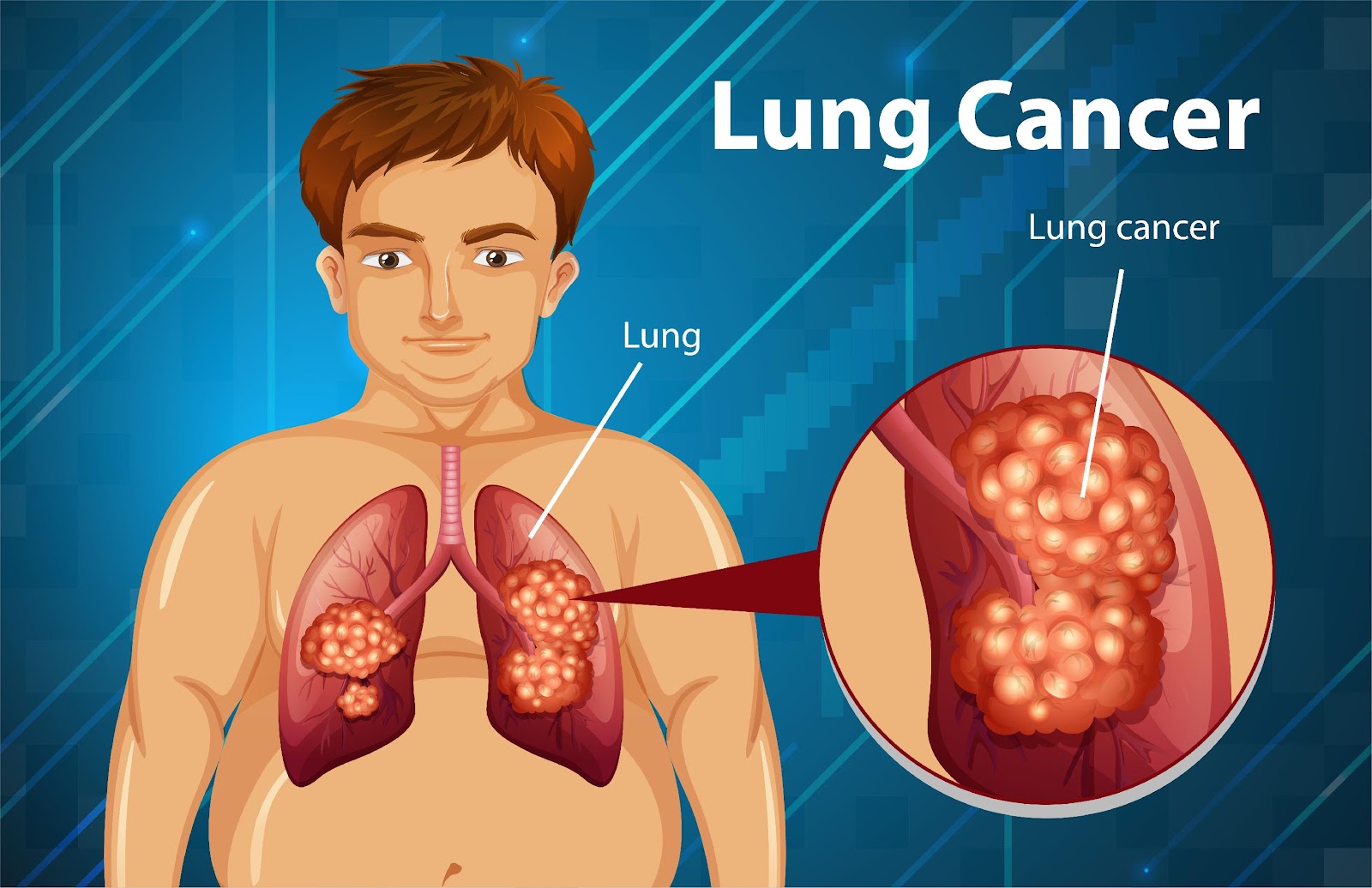
What is Lung cancer?
Cancer is a disease in which the body cells grow out of control. When cancer begins in the lungs it is called lung cancer. Lung cancer grows in the lungs and may expand to lymph nodes or other body organs, like brain. Cancer from other organs also advances to the lungs. When cancer cells expand from one organ to another they are called metastases.
What are the causes of Lung Cancer?
It is the rapidly dividing cells that eventually lead to lung cancer. Cell division is a normal process, but every cell has an inbuilt off switch that, when pressed, either hinders the cell from proliferating (senescence) or causes it to die off (apoptosis). When a cell suffers too many modifications or divisions, it activates the off switch (mutations).
Your body’s regular cells can become cancerous by undergoing mutations that take away the off switch. Unchecked cell multiplication causes problems to regular cell function. It is possible for cancer cells to enter your lymph nodes or bloodstream and travel throughout your body, causing further damage.
Mostly Smoking causes the lung cancer, both in smokers and the people around the smoker who are exposed to secondhand smoke. In certain cases lung cancer can happen in people who never smoked or were never exposed to secondhand smoke but in some cases there is no clear cause for lung cancer.
Doctors emphasize that in some people smoking causes lung cancer by damaging the cells that line the lungs. Changes in the lung begin abruptly when you inhale cigarette smoke (carcinogens).
Initial symptoms of lung cancer:
Initial signs and symptoms of lung cancer are:
- Persistent cough:
Be cautious for a persistent, new cough. A cough brought on by a cold or respiratory infection will usually go away after a week or so, but a chronic cough that does not go away could be a sign of lung cancer.
And, keep an eye out for any modifications to a persistent cough, especially if you smoke. Consult your doctor if your cough:
- Lingers
- Happens more frequently
- Has gotten intense
- Sounds hoarse
- Produces blood
- Lots of mucus
- Wheezing or changes in breathing:
Irregular or an increased vulnerability to fatigue is further signs of lung cancer. Breathing problems may arise from an airway obstruct or shrinkage caused by lung cancer, or by a formation of lung tumor fluid in the chest. When you start to feel tired or out of breath, notice it. Don’t dismiss it if you experience breathing difficulties after doing activities you used to find simple or after climbing stairs.
When you breathe, your lungs may make a wheezing or whistling sound due to constriction, obstruction, or inflammation of your airways. There are various explanations for this, some of which are benign and readily treated.
Nevertheless, wheezing may also indicate lung cancer, so it’s good to bring it up.
- Body ache:
Lung cancer can cause ache in the chest, shoulders or back. This happens when you cough all day. Immediately tell your doctor if you come across this type of chest pain:
- Sharp
- Dull
- Persistent
- Intermittent
Keep a check whether it is restricted to a specific area or happening throughout the chest. When lung cancer results in in chest pain, the discomfort may happen from increased lymph nodes or metastasis to the chest wall, the lining around the lungs or the ribs. Lung cancer that has reached to the bones may cause back pain or the other areas of your body. Bone ache is worse at night and intensifies with movement. Headaches can be an indication that lung cancer has spread to the brain. Remember! Not all headaches are linked to brain metastases.
- Scratchy and hoarse voice:
If you hear a prominent change in your voice or if someone tells you that your voice sounds hoarse or scratchy, it is better to meet your doctor. Persistent hoarse voice hints at something more serious. Sometimes hoarse voice can be linked to lung cancer because tumor harms the nerve that controls the larynx or voice box.
- Unexpected weight loss:
Other types of cancer including lung cancer can cause unexpected weight loss of 10 ponds or even more. As a result of cancer this sudden loss in weight can happen from cancer cells consuming energy. It could also happen from the changes in the way body uses energy from food. It is significant not to ignore a change in your weight.
Less frequent signs and symptoms:
Less common symptoms of lung cancer are:
- Finger clubbing
- Problem in swallowing
- Inflammation on face and neck
- Blood cots
Small cell lung cancer symptoms:
Small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer are the two main types of lung cancer. SCLC is less prevalent than NSCLC but more destructive. SCLC has no initial apparent symptoms but when it spreads within the lung or to the other parts of your body, you may suffer from the following:
- Bloody mucus
- Irregular breathing
- Chest pain
- Constant cough
- Loss of appetite
- Facial inflammation
Consult your doctor in case of these symptoms.
Advanced lung cancer symptoms:
In advanced stages of lung cancer, the cancer generally grows to both lungs and other organs, such as bones or brain. The symptoms of advanced lung cancer are:
- Fatigue
- Pain and discomfort
- Breathing issues
- Constant cough
- Loss of appetite
If cancer is spread to your bones or brain then you may have symptoms like fractures or vision issues.
Linked syndromes:
Lung cancer created groups of some symptoms that are called syndromes. Some of them are Horner’s syndrome, superior vena cava syndrome and paraneoplastic syndrome.
Symptoms of Horner’s syndrome:
- Weekend or drooping eyelid
- Smaller pupil in that eye
- Little or no sweating at that side of your face
- Excessive shoulder pain and discomfort
Symptoms of superior vena cava syndrome:
- Swelling on face, neck and upper chest, sometimes turning your skin bluish-red
- Headaches
- dizziness
Since superior vena cava syndrome is can be detrimental to health, immediately consult your doctor.
Paraneoplastic syndrome:
Some common Paraneoplastic syndromes are:
- syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Lamber-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
- Humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy
End-stage symptoms for lung cancer:
- Pain
- Confusion
- Fatigue
- Restlessness
- Loss of appetite
- Cough
- Concentration problems
- Irregular breathing
- Shortness of breath
- A rattle in the chest in between breaths
- Anxiety and depression
- Loss of consciousness
Conclusion:
Lung cancer begins in the lungs and eventually spread to the other parts of the body. There is no certain way to prevent lung cancer but by quitting smoking, you can drastically lower your chance of developing lung cancer. Lung cancer treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy and radiation.