Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
A urinary tract infection is a disease of the urinary system. It is an infection caused by microbes, which are tiny microscopic organisms. Generally UTIs are created by bacteria, some fungi and infrequently by some viruses.
What are urinary tract infections?
Urine is a byproduct of metabolisms in humans or you can say that urine is a byproduct of the kidneys. Kidneys make urine by decontaminating urea and excess water from the blood. Generally urine moves through our urinary system without any infection. Urinary tract Infection and inflammation can happen because of the bacteria present outside from the body because our urine does not contain bacteria. UTIs are the most usual human infections.
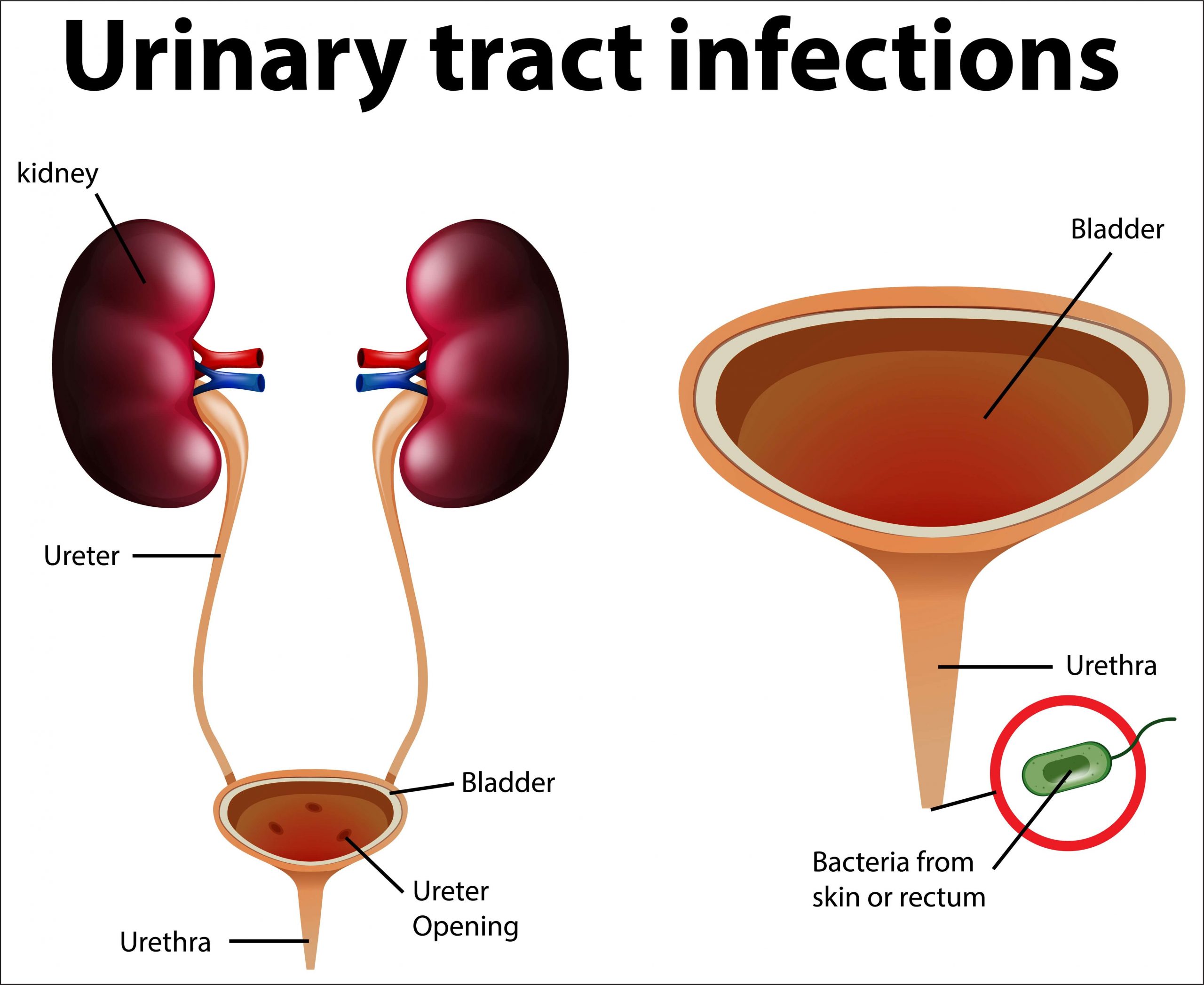
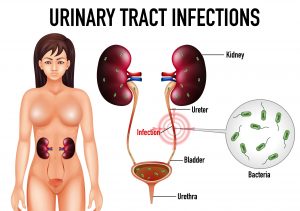
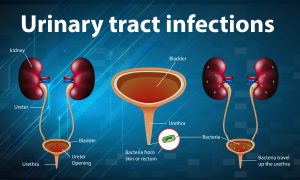
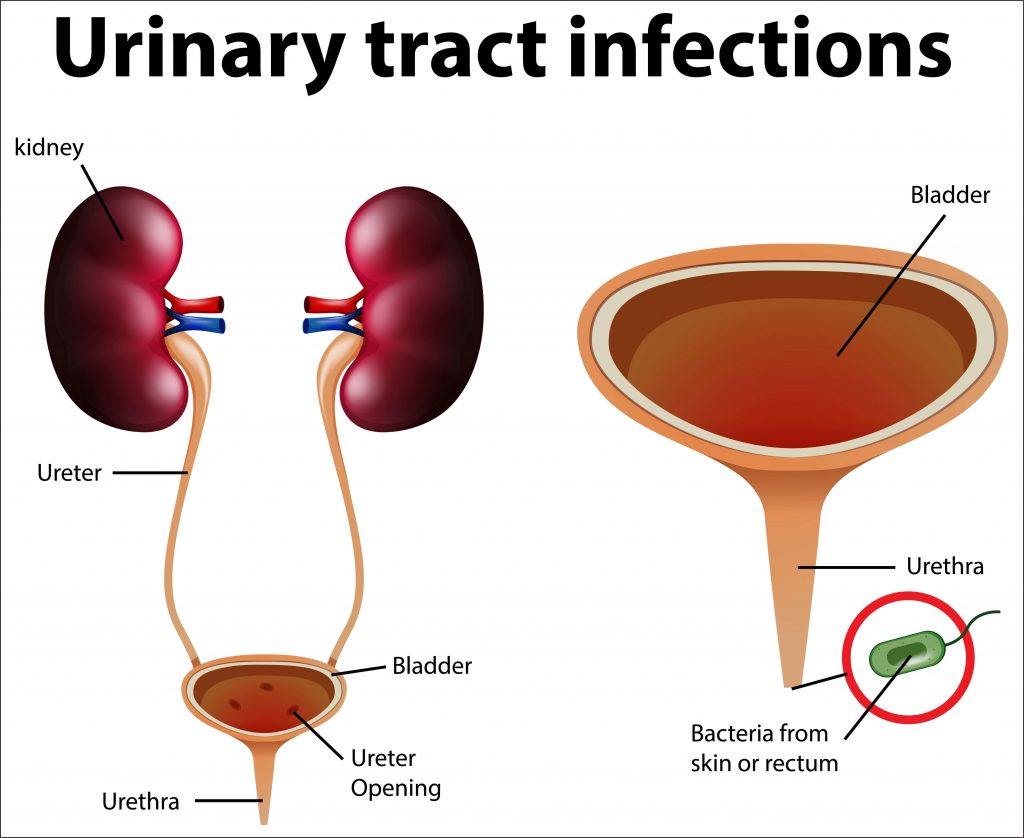
Urinary tract and its parts
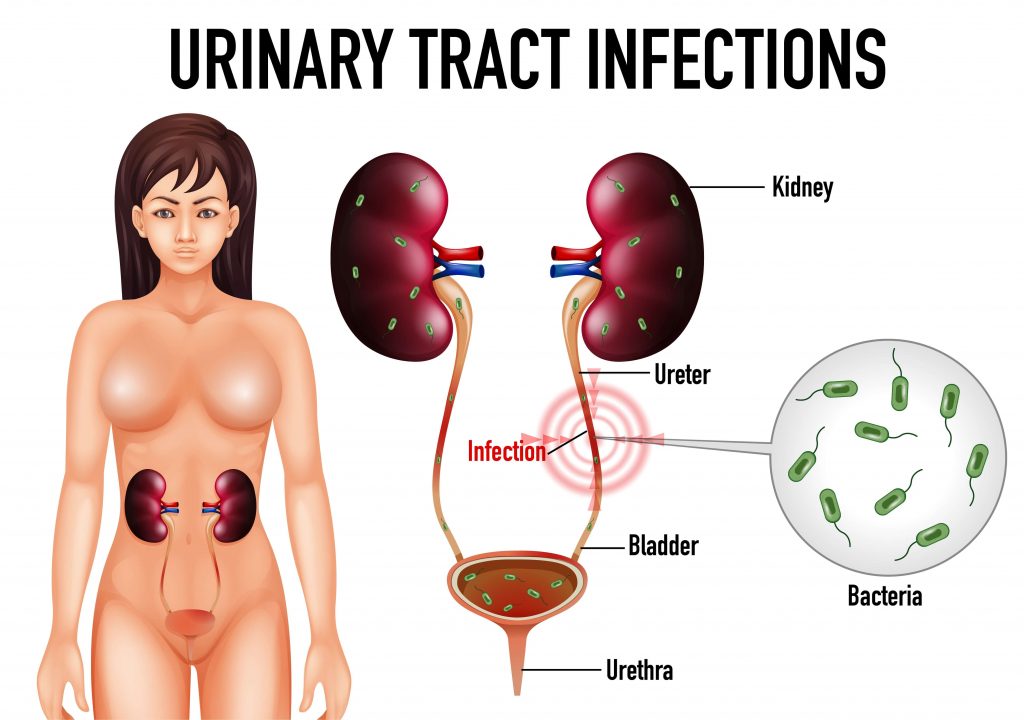
Urinary system makes and removes the urine or liquid waste from the body. Basically Urinary system is the filter of your body which removes toxins through urination. Urinary system includes:
- Kidneys are little organs that work continually. They are located on the back of your body just below the rib cage. They filter your blood by removing waste and water. This waste is your urine.
- Ureters are thin tubes inside your pelvis that carry urine from kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder is an empty, pouch like container that holds your urine. It is made up of muscle. Your bladder enlarges as it fills up. Generally bladders can store up to 2 cups of urine.
- Urethra this tube takes urine from your bladder to the out of the body. This tube leads to penis in men which is an opening outside of your body and vagina in women.
The bladder and urethra (lower urinary tract) is more prone to infections than the upper urinary tract. Being a woman the odds of getting UTIs are higher than any man. Women can have recurrent infections for several years. Only1 in 10 men have the possibility to get UTI in their lifespan.
In this infection you need to urinate time and again. While passing urine you have a burning sensation, lower back or side ache, which is often treated with antibiotics.
Types of urinary tract infections
Infection can be anywhere in your urinary tract. Enlisted below are some types of UTIs:
- Cystitis
It hurts when you pee, you feel like urinating over and over. This infection can have lower back ache, murky or bloody urine.
- Pyelonephritis
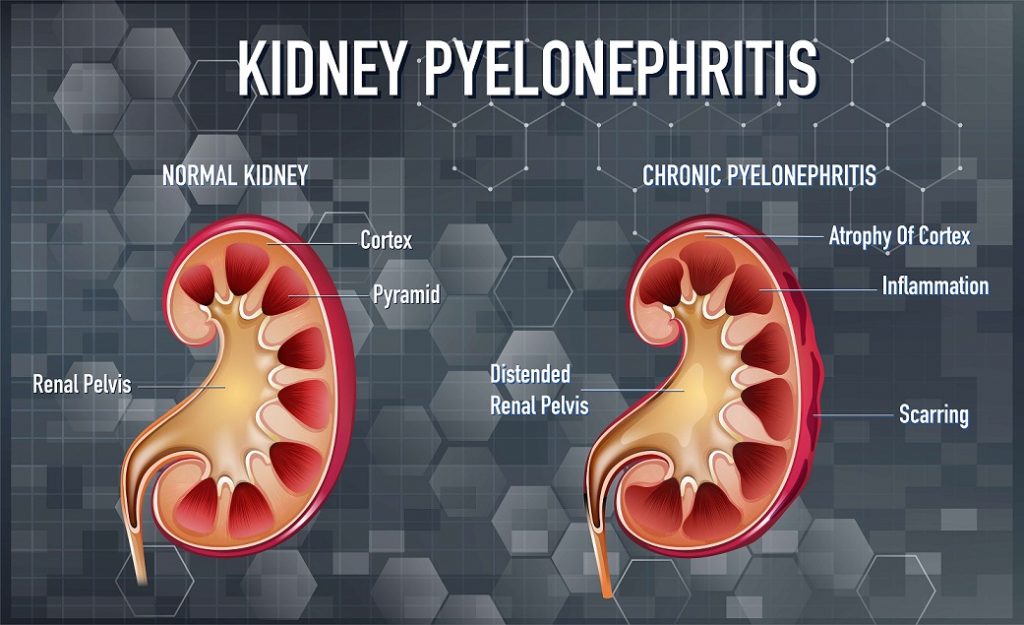
You get chills, fever, nausea, vomiting, foul smelling urine, pain in back or groin and frequent urination.
- Urethritis
This causes unusual vaginal discharge, itchiness, inflammation and pain while peeing.
Who is susceptible to urinary tract infections?
Women are more prone to UTIs, but anyone can have this infection. Women are more susceptible to UTIs because urethra in women is smaller and adjacent to the anus, where (E. coli) bacteria are prevalent. Older grownups have greater chance for developing cystitis. This is because of the undone vacating of the bladder. There can be other various medical conditions like enlarged prostate or a bladder prolapse, linked to it. Consult to your doctor if you get perennial UTIs. You doctor will run up some tests to check if you have any other diseases like abnormal urinary system or diabetes that contribute to your infections. People having repeated UTIs are given moderate dosage of antibiotics to fend off infections from coming back. This treatment is not done frequently because you can develop resistance to the antibiotics.
Causes of urinary tract infection
Microorganisms generally, bacteria are the creators of UTIs. Bacteria enter urethra and bladder, triggering inflammation and infection. Mostly you get infection in the urethra and bladder but sometimes, bacteria affect your kidneys by entering ureters. Most of bladder infection (cystitis) cases are caused by a bacterium found in the intestines called E. coli. UTI is the core reason why doctors guide women to clean from front to back after urinating. Since Urethra is close to anus. Sometimes bacteria from the large intestine, E. coli, can exit from anus and enter your urethra. From there, it can move to your bladder, damaging your kidneys, if not treated in time.
Women are more susceptible to UTIs because of their genes. A bacterium comfortably travels to women bladder because they have shorter urethras than men. Women having diabetes and other health conditions like hormone changes, multiple sclerosis, kidney stone that hampers urine flow, stroke or spinal cord injury are at greater risk because of their feeble immune system.
Urinary tract infection diagnosis
Generally doctor will conduct certain following tests to detect UTI:
- Urinalysis:
Urinalysis is a single sample urine test. It is a visual, chemical and microscopic examination of your urine. Urine is examined for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria to diagnose any infection. Urinalysis is done for diabetes, liver disease, kidney ailments and to diagnose UTIs.
- Urine culture:
Urine culture is a simple but significant lab test to identify the type of bacteria or germs in your urine.
- Ultrasound:
Your doctor will go for more tests like ultrasound, if the infection does not ward off. Ultrasound is also called sonography. In this high-intensity sound waves create an image that depicts the inside of your body. This test is carried out on top of your skin, without any preliminary preparation and is pain free.
- Cystoscopy:
Urologist uses a special instrument called cystoscope to visually discern inside the bladder and urethra.
- CT scan:
It is an imaging test. CT scan is a type of X-ray that takes samples of the body. This test is much more detailed and error-free than other X-rays.
Chronic UTIs
You need a thorough treatment if you have a history of repeated UTIs. Some of the options are as following:
- A mild dosage of antibiotic for a long period to avert recurrent infections.
- One dose of antibiotic after intercourse. Sex often aggravates infection.
- Antibiotics for a day or two whenever, symptoms occur.
- Non-antibiotic prophylaxis treatment.
You doctor may suggest some common tests to diagnose chronic UTIs before any treatment:
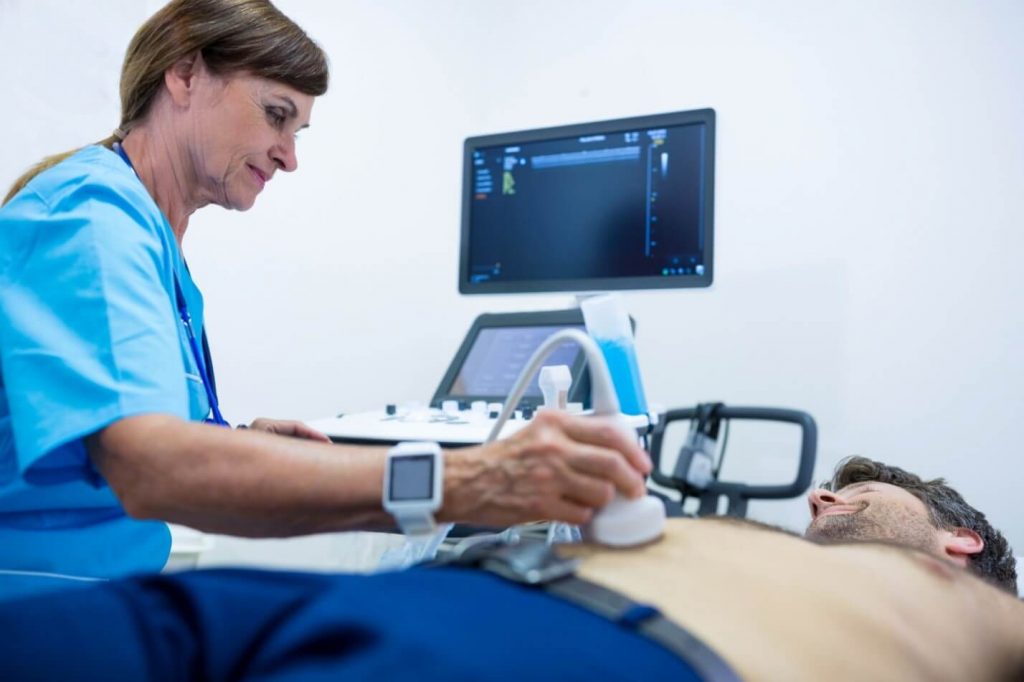
- Ultrasound
- Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
- Cystoscopy
- CT scan
Symptoms of urinary tract infection
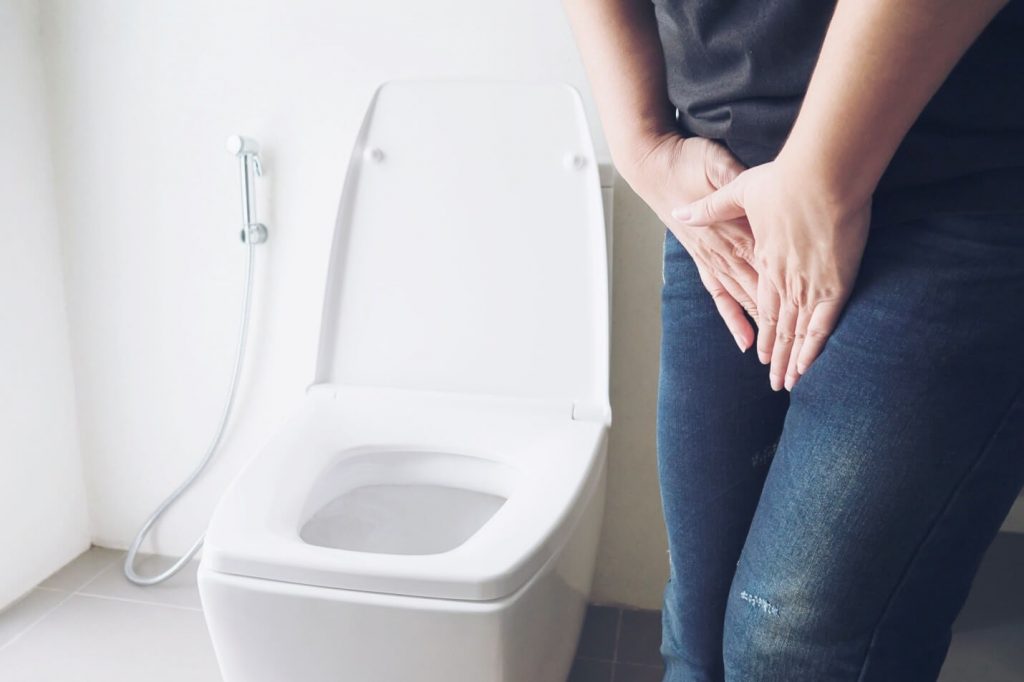
UTI symptoms depend on the infected part of the urinary tract. Infection makes the infected part swollen and irritated. Some of the symptoms are mentioned below:
- Pain in the abdomen, flank and pelvic area
- Pressure in the pelvis area
- Recurrent urination with small amounts, having urge to pee more than usual, urine leakage
- Discomfort or blood when urinating
- Need to urinate at night
- Cloudy and bad-smelling urine
- Pain during intercourse
- Rectal pain in men
- Weariness
- Vomiting
- Chills and fever
- Inability to think clearly
Treatment of Urinary tract infections

Infection needs to be cured in time. The sooner the better. Lower urinary tract infection is facile to treat. Upper urinary tract infection is much more complex to treat and can spread into your blood leading to sepsis. This situation is quite alarming. Immediately consult your doctor with the onset of UTI symptoms. Usually Antibiotics are used to treat urinary tract infections. Antibiotics combat bacteria. Your doctor will choose the best suitable antibiotic to treat the specific bacteria causing infection. Some frequently used antibiotics are:
- Sulfonamides
- Nitrofurantoin
- Amoxicillin
- Cephalosporins
- Trimethoprim
- Doxycycline
- Quinolones
Fluoroquinolones is another antibiotic and generally is not advised for UTIs because it has Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin because their risks surpass the benefits for treating simple UTIs. Your health care provider might suggest fluoroquinolone.

Cranberry juice often assists in preventing UTIs. Red berry has tannin that combat E. coli bacterium, which sticks to the walls of your bladder causing UTIs.
Follow your healthcare instructions for taking the medicines. Don’t stop taking medicine once you feel better because the infection can return. It is imperative to take antibiotics religiously and complete the antibiotic course. Drink plenty of water to wash off bacteria from your body. Your doctor might suggest heating pad or some pain killers. Patient with a history of persistent UTIs is given antibiotic on the initial symptoms. Some patients are recommended to take medicines everyday or after every intercourse to avert the infection. Discuss with the doctor about the best possible treatment if you have a history of frequent UTIs. Specialists are looking up for novel ways to cure and shut out UTIs, such as vaccines, some immune system boosters and hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women.
Prevention
Following tips can help you from getting UTI:

- Plenty of water: drink ample water to avert infections. Drinking plenty of water flushes the bacteria out of your body.
- Good hygiene: good hygiene plays a significant role in preventing UTI especially in women. Always clean from front to back after urinating or bowel movement.
- Avoid foods and fluids that could irritate your bladder: alcohol, citrus juices, caffeinated drinks and spicy foods should be avoided.
- Cranberry juice: many people find cranberry juice really soothing and healing.
- Immediately empty your bladder: empty your bladder before and after sex.
- Avoid products in genital area: avoid spray, deodorant or powder in the genital area because this can irritate urethra.
- Reconsider you birth control method: diaphragms, lubricants or certain condoms treated with spermicide can lead to bacterial growth.
- Change you clothing style: Your tight fitted clothes can spike chances of a UTI. Tight clothes can rub your skin causing chafing, inflammation and infection.
Conclusion:
UTIs are very common. This infection involves bladder, urethra, ureters or kidneys. Usually infection is caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. Instantly consult your doctor for diagnosis and correct treatment.