Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
What is appendicitis?
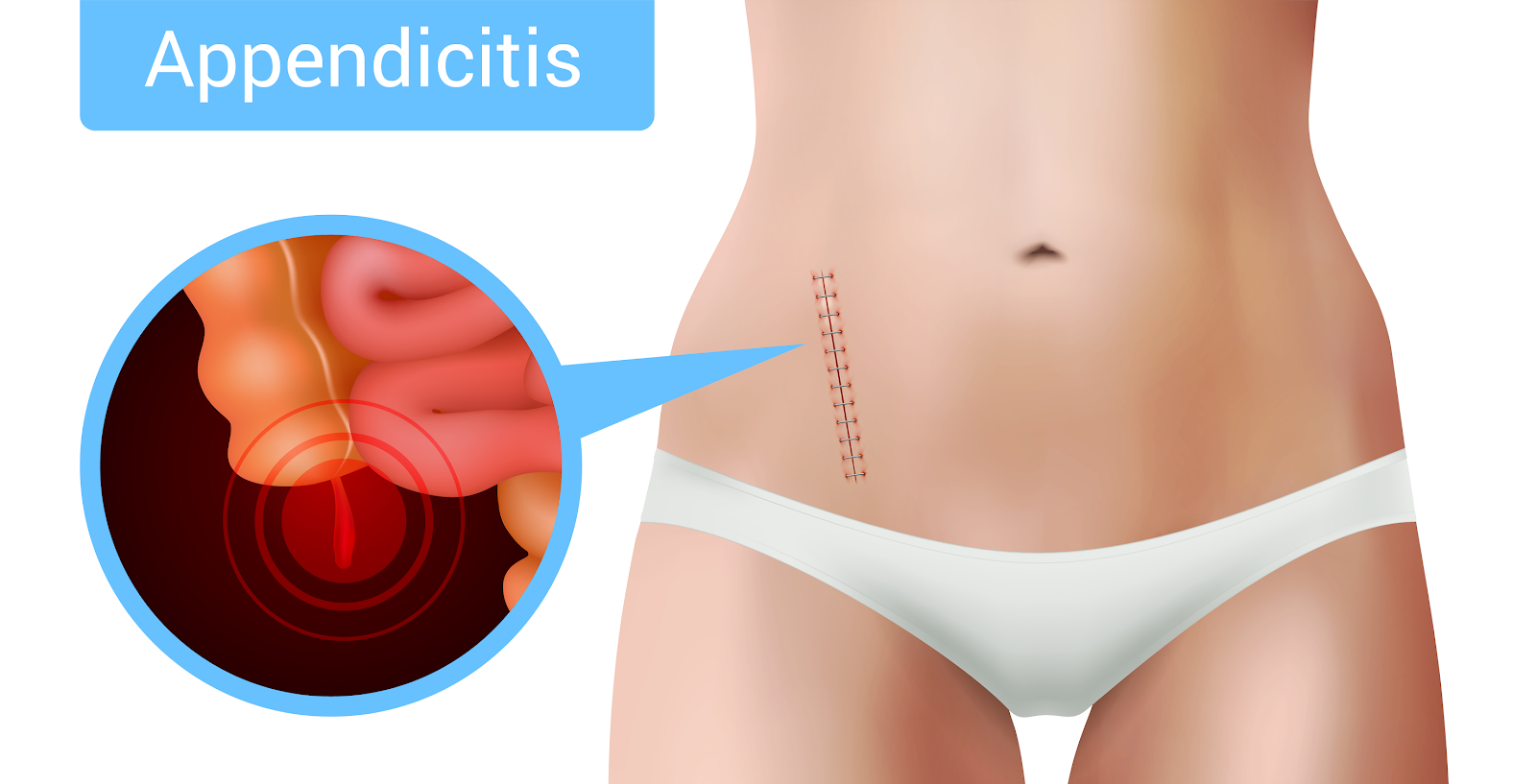
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix which is a small finger-shaped, tubular pouch that projects from your colon on the lower right end side of your abdomen. Your feces move through your large intestine can obstruct or infect your appendix which leads to swelling. It causes grave pain in your lower abdomen and can burst. Generally people feel agony and discomfort around the navel. It spreads bacteria throughout your abdominal cavity from inside your bowels causing sepsis which is a perilous condition.
Unfortunately anyone can have appendicitis; mostly it develops in people between 10 and 30 years of age. It is a medical emergency and needs a prompt surgery to eradicate the appendix. Fortunately your appendix is not a significant organ and you can easily survive without it.
Where is an appendix located?
Appendix is 31/2 finger shaped, long tube of tissue protruding from your large intestine on the lower right side of your body. The appendix has designed tissue that can create antibodies, but we are unclear about the role of appendix in our body.
Causes of appendicitis:
Appendicitis is the result of an obstruction in the lining of the appendix usually by poop, an external body or cancer. Obstruction can be caused from some infection or bacteria and as a result your appendix becomes inflamed and filled up with pus that ruptures your appendix. Some of the known causes are:
- Appendicoliths: facaliths, appendicoliths or appendix stones are the hard, calcified fecal deposits and get clogged in the opening of your appendix. They convey bacteria and can also catch the bacteria that are already present in your appendix.
- Lymphoid hyperplasia: your lymphatic system which is a part of your immune system helps combat infections by creating and releasing white blood cells into your tissues. This inflames the lymphoid tissue in your appendix, even when the real infection is somewhere else in your body. The puffed tissue in your appendix can block it, leading to the infection from the inner side.
- Colitis: you appendix is troubled by the swelling in your infected colon or inflammatory bowel disease. The infection may advance or the inflammation itself may agitate.
Other factors that are responsible for the obstruction in the opening of your appendix are tumors, parasites, cystic fibrosis.
Chronic appendicitis:
Chronic appendicitis is something that mild inflammation occurs periodically for a prolong time. It can be an acute condition like inflammatory bowel disease or mild bacterial excessive growth or it can be a blockage that transfers in and out of the opening to your appendix.
How common is appendicitis?
Appendicitis is very common between the ages of 10 and 30. In children it is frequent during the teen years but younger kids also get appendicitis. It is uncommon in kids younger than 2 years old. In the U.S. almost 5% of the population will get chronic appendicitis in their life.
Symptoms of appendicitis:
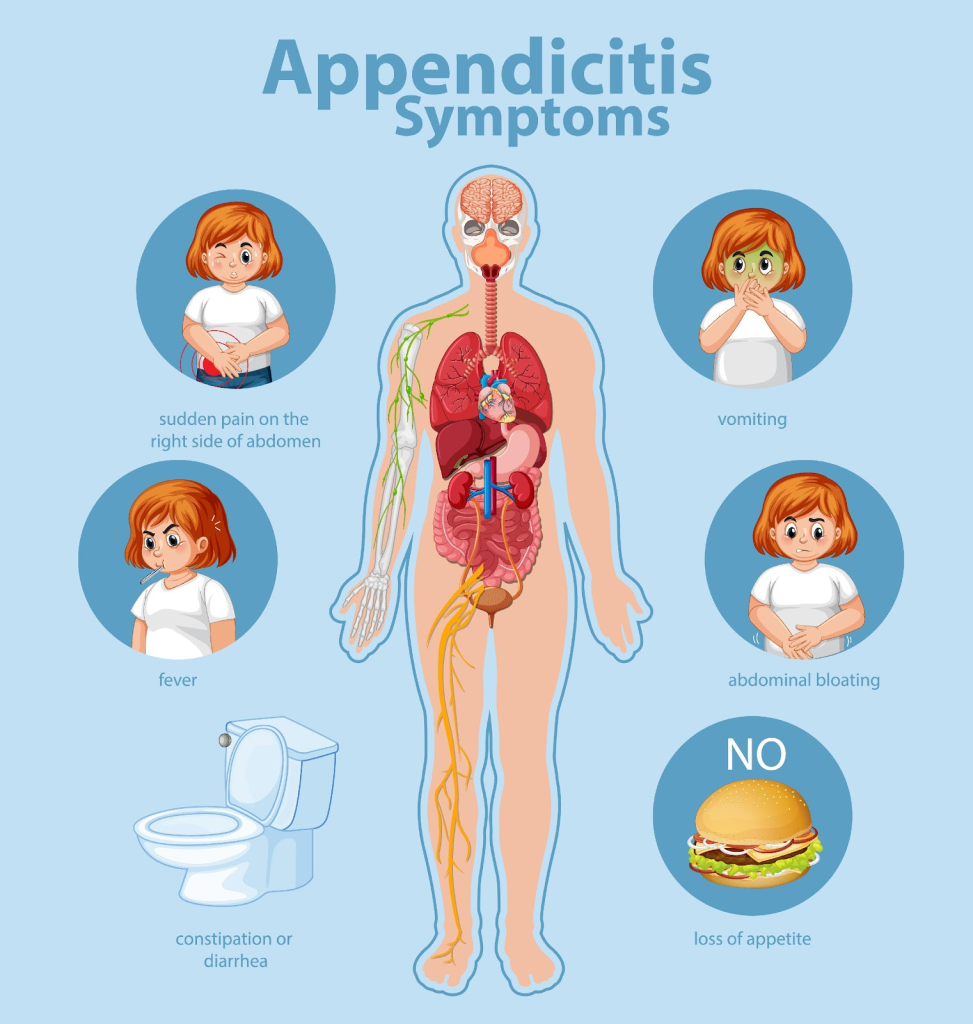
If you have any of the following symptoms immediately consult your doctor. Well timed diagnosis and treatment is very significant and avoid taking homemade remedies, drinking, antacids, laxatives or heating pads.
Symptoms of appendicitis:
- Discomfort in lower right belly or pain near navel that travels lower, this is one of the early signs.
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting after the onset of belly pain
- Swollen belly
- 99-102 F fever
- Difficulty in passing gas
Some of the uncommon symptoms are:
- Severe pain in lower or upper belly, back or near end
- Difficulty in peeing
- Vomiting
- Intense cramps
- Constipation or Diarrhea with gas
- Flatulence abdominal bloating
- Bowel paralysis
- malaise
The intensity of your pain may vary from person to person and depending on your age and position of the appendix. During pregnancy the pain starts from the upper abdomen because of the higher position of appendix.
Appendicitis complications:
Unattended, swollen appendix will rupture, swarming bacteria and debris into the abdominal cavity, the central part of the body holds your liver, stomach and intestines. This can lead to a chronic inflammation of the abdominal cavity’s lining called peritonitis. If left untreated it can be life-threatening. At times an abscess develops outside a puffed appendix. An abscessed appendix can rupture and cause peritonitis.
Tests that can help diagnose appendicitis:
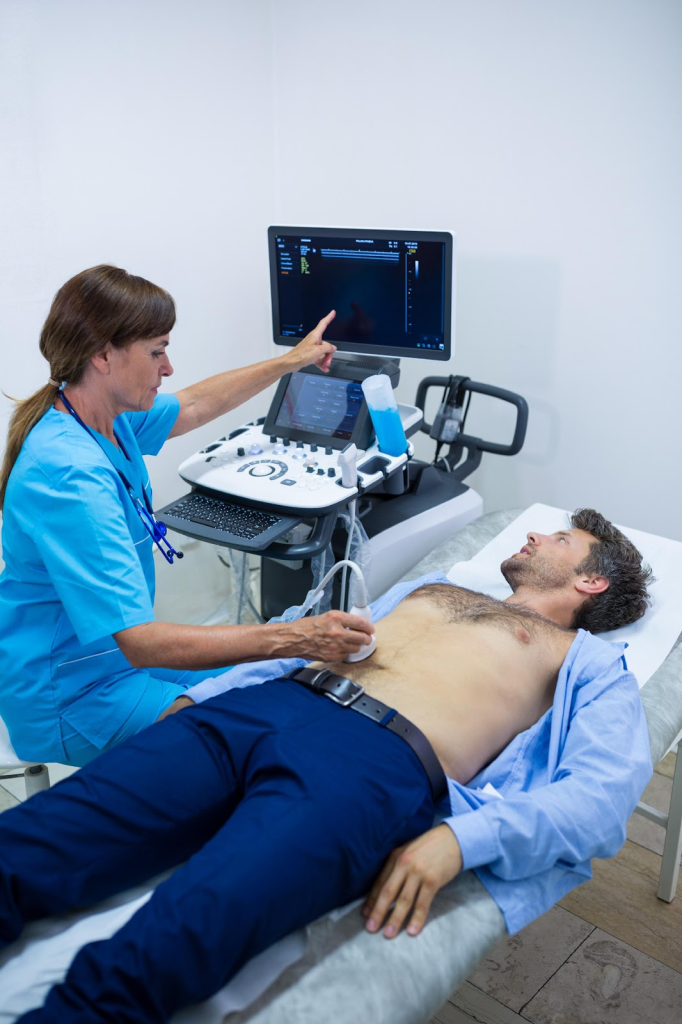
Blood tests and imaging tests are done for appendicitis. Blood tests can reveal signs of inflammation such as white blood cell count or C-reactive protein count and they disclose any infection. Imaging tests like abdominal ultrasound or a CT scan reveal if your appendix is puffed or irritated. Some other test might be done to get a more clear idea about this condition.
Conclusion:
We cannot avert appendicitis but it can be uncommon in people who eat fiber enriched foods such as fresh fruits and vegetables. We do not consider Appendix that significant until one day it starts hurting and causing some great discomfort. If that happens then you must not waste a single minute, immediately rush to your doctor. Appendicitis is a very common and grave condition which requires emergency surgery. Once your appendix is eradicated you will never have to fret over it again.