Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
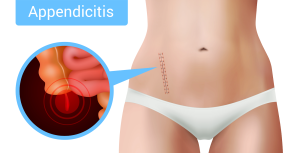
Appendicitis:
Appendicitis is a painful and discomforting medical condition in which the appendix is swollen and filled with pus. Pus is an amalgamation of dead cells and swollen, infected tissues. Appendicitis causes abrupt sharp abdominal pain which needs immediate medical treatment.
What is appendix?

Appendix is a 2-4 inches small, thin tube connected to the large intestine, where poo forms. Blockage of the appendix leads to the appendicitis. If the obstruction continues the swollen tissues becomes infected with bacteria and perishes due to insufficient blood supply, which ultimately leads to the rupture or burst of appendix. If your appendix is infected it can burst within 48-72 hours after certain visible symptoms which is why it is considered an emergency condition.
Who can get appendicitis?
It can happen at any age but mostly appendicitis cases happen between 10-30 years of age. Appendicitis is very rare in children younger than 2 years old. In the U.S. 1 in 20 people will get appendicitis in their lives. Family history of appendicitis also elevates the risk of it. A Child having cystic fibrosis can also increase the risk of getting appendicitis. As a child your appendix is a part of your immune system but when you become older it stops doing so and the other parts of your body help to fight back infection.
Causes of appendicitis:

The exact cause of appendicitis is not known yet. In some cases it happens when something obstructs the entrance of the appendix. The entrance can be blocked by a small piece of calcified feces or an upper respiratory tract infection that causes lymph node within the wall of the bowel to swell. If the blockage causes swelling and irritation it could lead to the elevated pressure within the appendix and inflammation ceases the blood supply to the appendix which can rupture the appendix.
Numerous infections like virus, bacteria or parasites in your digestive tract can cause appendicitis. Sometimes tumors are also liable for appendicitis.
Symptoms of appendicitis:
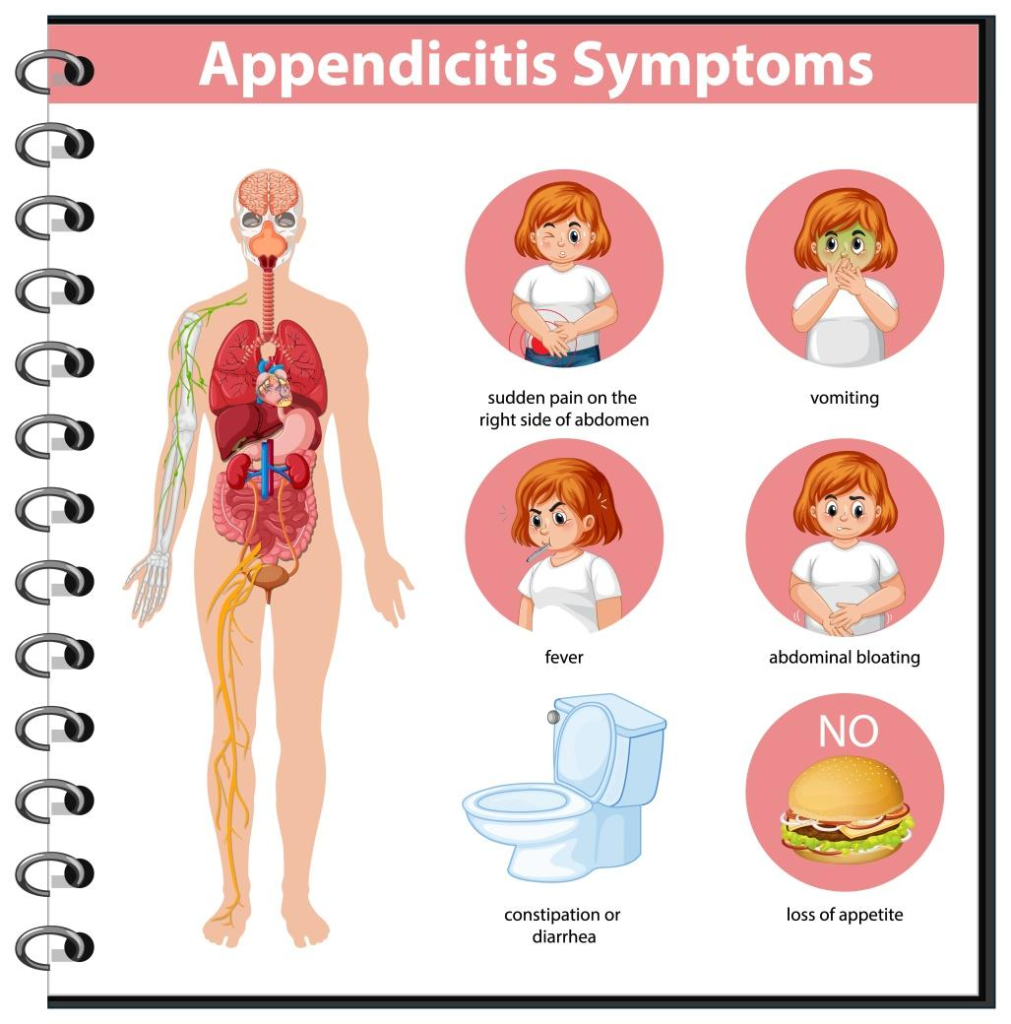
Initial signs and symptoms of appendicitis include an agonizing pain that commence around the belly button and then gradually confines over the lower right abdomen. Appendicitis ache intensifies over several hours and can aggravate when you move, breathe heavily, cough or sneeze. Some of other symptoms are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Difficulty in passing gas
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal swelling
- Low fever
Symptoms of appendicitis vary from person to person especially in children and pregnant women.
Diagnosis of appendicitis:
Sometimes prognosis of Appendicitis is quite deceitful. Symptoms are uncertain or similar to other illnesses like gall bladder problems, bladder or urinary tract infection, Crohn’s disease, gastric, kidney stones, intestinal infection and ovary problems. Certain tests can help determine appendicitis:
- Abdomen examination for inflammation
- Urine test to exclude UTIs
- Rectal exam
- Blood test
- CT scans
- ultrasound
Treatment for appendicitis:
The standard treatment for appendicitis is the surgery to eradicate appendix which is called an appendectomy.
Appendectomy:
The appropriate treatment for appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix before the appendix bursts. Prior to surgery the patients are given IV fluids to keep them hydrated. Later patient will not be permitted to consume any solids or liquids because it may lead to complications with anesthesia during the surgery. Surgery is generally done through laparoscopy, a small invasive procedure where small keyhole cuts are made on the abdomen and the appendix is eliminated with the aid of a small camera lead by the surgeon. In certain cases it is imperative to perform an open abdominal surgery to get rid of the appendix.
At times surgery for appendicitis displays a negative appendectomy with high rates in infants, elders and young women. The use of imaging studies has decreased the negative appendectomy rate to 7%-12%. The problem in making an absolute prognosis of this medical condition and the chances of missing a chronically swollen appendix and the patient becoming very ill due to the cut makes a certain rate of misdiagnosis ineludible. Especially women are at greater risk of negative appendectomy because ovarian and uterine problems make the prognosis more complicated. CT scan before the surgery has reduced this percentage to closer to 7%-8% in women.
Standard medicine for appendicitis:
If your physician suspects appendicitis, he will immediately eliminate the appendix to avert its rupture. Unfortunately if the appendix has developed an abscess you may have to follow two procedures:
- To do a CT-guided drainage of the pus and the fluid
- To eradicate the appendix 8-12 weeks later. This suspended surgery is called interval appendectomy.
Before an appendectomy antibiotics are given to combat the peritonitis or infection in the abdominal cavity’s lining. The appendix is eradicated through a brief incision in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen.
If you have peritonitis the abdomen is drained of pus. You are physically capable to get up and move around within the 12 hours of surgery and you can get back to normal routine activities in 2-3 weeks. Three to four little cuts are made if the surgery is performed with a laparoscope. With the help of this procedure the recovery is speedy.
Care after an appendectomy:
After the removal of your appendix keep your incision tidy and clean to boost healing procedure and avert infection. Follow the given instructions that your surgeon advised you to do.