Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is when your body fails to consume sugar into the cells to use it for the rest of the day, this leads to the accumulation of excess sugar in your bloodstream. It is an enduring health condition that affects your body functions.
Diabetes doesn’t let your body make sufficient insulin or your body can’t use it according to the requirement. Ample sugar stays in your bloodstream when there is inadequate insulin or the cells stop reacting to insulin. With the passage of time this can cause grave damage to body tissues and organs. It also leads to various health problems like heart diseases, vision loss and kidney ailments. Some significant points to know about diabetes:
- In US more than 37 million adults have diabetes and unfortunately, they are unaware of it.
- In US, diabetes is the seventh chief cause of death.
- Diabetes is the prime reason of kidney failure, lower-limb amputations and blindness in adults.
- In the last 20 years the number people suffering from diabetes has increased.
There is no specific treatment for diabetes but maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking a healthy, balanced diet can really help.
Different types of Diabetes:
You can have various types of diabetes. It doesn’t matter what type of diabetes you have, it can cause excess sugar in your blood. Redundant sugar in the blood can lead to acute+- health issues. Enlisted below are some of its types:
Type 1 Diabetes:
In this diabetes your body strikes itself, you can also call it an auto immune disease. Consequently, the insulin-producing cells present in your pancreas are damaged. Approximately, 10% of diabetic patients have type 1. It can be diagnosed at any age. It’s generally distinguished in kids and young adults which is why it is also called juvenile diabetes. Type 1 diabetic patients are totally dependent on insulin and need to take insulin regularly.
Type 2 diabetes:
In this type your body cells fail to respond to insulin or your body doesn’t create ample insulin. It is the most frequent type of diabetes. Probably 95% diabetic people have Type 2. There are 29 million people in U.S. having Type 2 diabetes. This happens in middle-aged or aged people. It can also be called adult-onset diabetes or insulin-resistant diabetes. Because of childhood obesity Type 2 diabetes hit kids and teenagers as well.
Gestational diabetes:
Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women because of high blood sugar during their pregnancy. Placenta producing insulin blocking hormones results in this type of diabetes. Yearly it influences up to 10% pregnant women in the U.S. gestational diabetes clears off after giving birth. In the later life, the unborn child is also at the danger of getting Type 2 diabetes. You can take some preventive measures for you and your baby to stay healthy.
Prediabetes:
You can say that it is a stage before Type 2 diabetes. Your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be categorized as Type 2 Diabetes. In U.S. 96 million adults have prediabetes. Mostly people are not aware of the fact that they have it. Prediabetes raises the chance of Type 2 diabetes, heart disease and stroke. Fortunately, if you have prediabetes you can reverse it by adopting healthy diet and healthy lifestyle.
Causes of diabetes:
The cause of types of diabetes is undetermined. The cause of diabetes is having plenty of glucose in your blood because pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin. Nevertheless, the type of diabetes affects the glucose level in your blood.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes:
Your body strikes and damages the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas, without insulin to permit glucose to enter your cells; glucose accumulates in your blood. This is an immune system disease. In some patients Genes play a significant role. A virus may activate the immune system attack.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes:
Your body cells don’t let insulin work as it should let glucose into its cells. Your body cells become insulin resistant. Your pancreas fails to cope and make ample insulin to overcome this resistance. Glucose levels elevates in your blood stream.
Gestational Diabetes:
Your body cells become defiant to insulin by the hormones created by the placenta during your pregnancy. Your pancreas can’t make required insulin to conquer this resistance. Excess glucose stays in your blood.
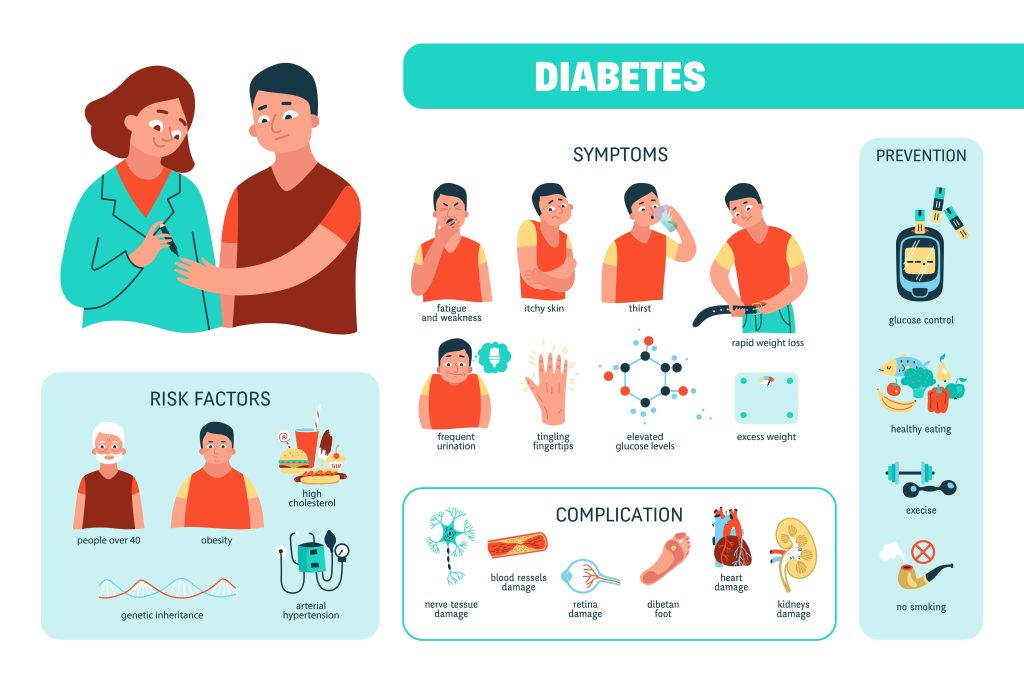
Symptoms of Diabetes:

Some of the visible symptoms are mentioned below:
- Dehydration
- Timid, exhausted feelings
- Blurred vision
- Senselessness or tingling in hands and feet
- Sores or wounds that fail to heal
- Unintended weight loss
- Recurrent urination
- Frequent infections
- Dry mouth
- Itchy and dry skin in women
- Yeast or urinary tract infections
- Erectile dysfunction and less sex drive in men
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes:
Symptoms can develop swiftly over a period of few days or months. Symptoms start off at a young age such as teenage or young adult. Further symptoms consist of vomiting, nausea, stomach aches and yeast or urinary tract infections.
Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes:
At first you may fail to detect the symptoms because they grow gradually with the passage of time. Symptoms are visible when you are a grownup adult but in prediabetes and Type 2 is on the peak in every age group.
Symptoms of gestational diabetes:
There are no obvious symptoms of gestational diabetes. Between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy, obstetrician will get you tested for gestational diabetes.
Prevention:
You can’t prevent or reverse Type 1 diabetes. But adopting a healthy lifestyle can help treat other type of diabetes. Try to follow certain things:
- Be more physically active
- Eat healthy diet
- Try to lose your weight if you are obese.