Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
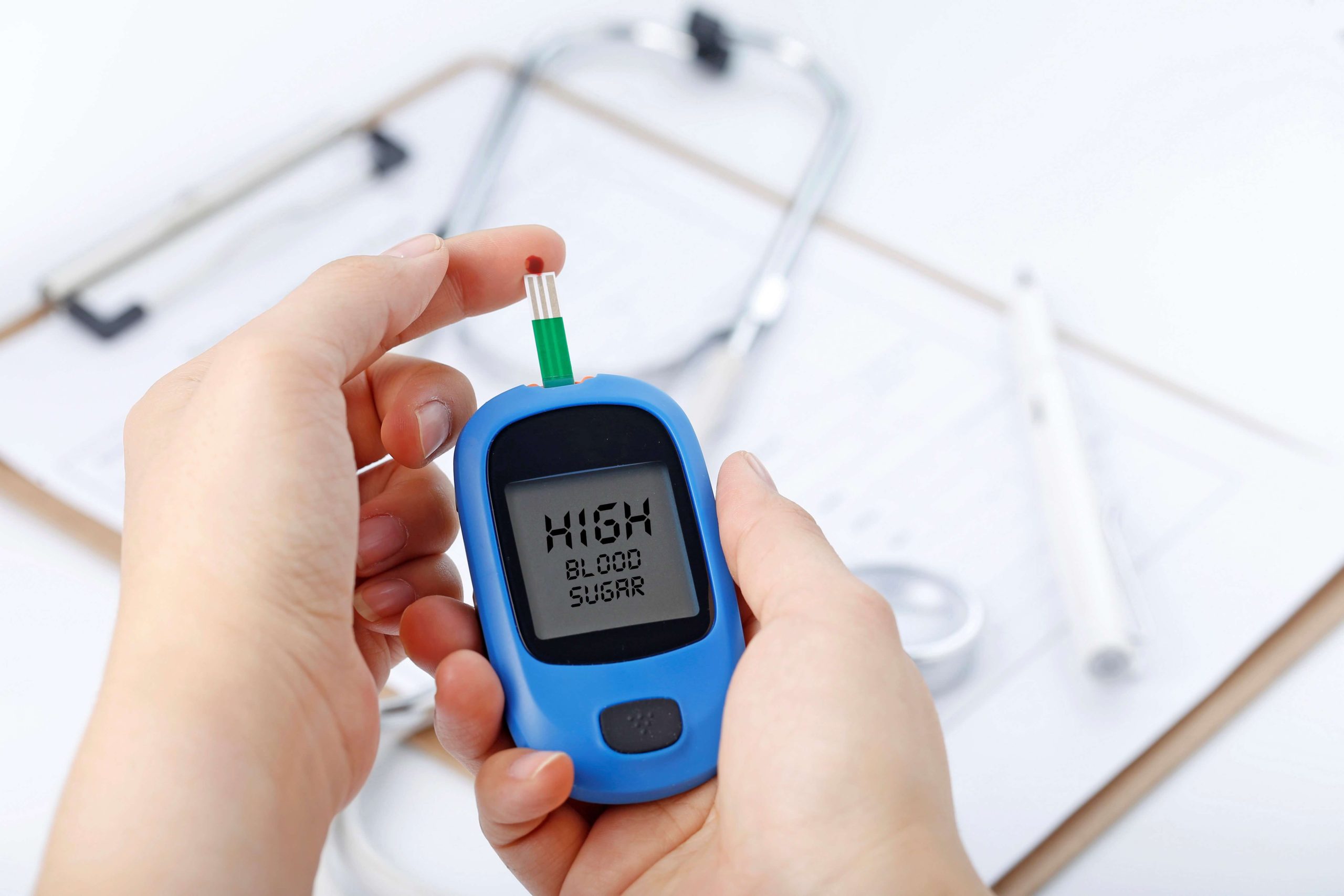
Diabetes mellitus also known as diabetes is a metabolic illness that seeds high blood sugar. Insulin is the hormone that controls the blood glucose. Glucose is the significant source of energy for the cells that build up muscles and tissues. Glucose also works as a fuel for the brain. Diabetic patient’s body either doesn’t make sufficient insulin or cannot use the insulin it produces. Hyperglycaemia (raised blood sugar) is a common result of unchecked diabetes. There are different types of diabetes but every type of diabetes can raise sugar level in the blood, leading to several critical health problems for example harming your nerves, eyes, kidneys or other organs.
Why insulin is important in diabetes?
Our body is made up of numerous cells. For energy these cells require food. Whatever you eat or drink it is broken down into simple sugar called glucose. Then glucose moves through blood to the body cells where it can be consumed to provide energy that our body needs daily. Insulin regulates glucose in our blood. Pancreas regularly releases insulin in little amounts. Pancreas release more insulin to send more glucose to your cells, when the amount of glucose in your blood reaches to a specific level. This drops your blood glucose levels. To evade blood glucose levels from decreasing your body alerts you to eat and release some of the glucose that’s kept stored in the liver. A Diabetic person doesn’t make insulin or their body cells are insulin resistant, resulting in elevated sugar levels circulating in the blood stream which is called high blood sugar.
Diabetes is like having a blood glucose level of 126 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) after an overnight fasting.
Types of diabetes:
There are different types of diabetes and they have different causes, symptoms and treatments:
- Type 1 Diabetes
It is an autoimmune disease which means your body charges itself. Beta cells which are insulin producing cells of the pancreas are demolished by the immune system. Probably up to 10% diabetic people have Type 1. It was once called “juvenile” diabetes because generally it is diagnosed in children and young adults. People with Type 1 need to take insulin regularly. You can also call it insulin dependent diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes
This is the most typical type of diabetes. In this your body becomes insulin resistant and sugar accumulates in your blood. It is the most frequent type. Possibly 95% people suffering from diabetes have Type 2. You can call it adult-onset diabetes because it eventuates in middle-age or old-age people.
- Gestational Diabetes

Gestational or hyperglycaemia arises during pregnancy. It is high glucose during pregnancy. Generally gestational diabetes departs after pregnancy. Pregnant Women having gestational diabetes are at a greater risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and can come across many impediments during pregnancy and delivering the baby. There is a possibility that later, their children are also at the risk of Type 2. Prenatal screening is the way to diagnose gestational diabetes.
- Prediabetes
Prediabetes or impaired glucose tolerance happens when your sugar level is higher than usual, but it is not that much high to be classified as Type 2 diabetes. This happens when your body cells don’t greet insulin the way they should and can lead to Type 2 diabetes. 84.1 million U.S. adults have sugar levels above normal but are not high enough to be labeled as diabetes. Prediabetes usually occurs without any visible symptoms but, complications like heart ailment linked with diabetes can also appear in people with prediabetes. It is necessary to consult your doctor for prediabetes to evade other ailments like Type 2 diabetes or heart disease.
Diabetes symptoms

Diabetes is the result of increased sugar in the blood. Some of the common symptoms are mentioned below:
- Increased appetite
- Polydipsia
- Weight loss
- frequent urination
- blurred vision
- tiredness
- wounds and sores that heal slowly
- less sex drive in men
- erectile dysfunction
- weak muscle strength
- vaginal dryness
- UTIs in women
- Yeast infections
- Dry, itchy skin
Type 1 diabetes symptoms
- Excessive hunger
- Extreme thirst
- Sudden decrease in body weight
- Recurrent urination
- Blurry vision
- Fatigue
- Mood swings
Type 2 diabetes symptoms
- Severe hunger
- Increased thirst
- Excessive urination
- Lack of vision
- Fatigue
- Wounds that recover slowly
- May cause recurring infections because of increased glucose levels
How to prevent the onset of diabetes

A healthy lifestyle helps to evade or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes. To avoid any complications one should:
- Try to keep a healthy body weight.
- Try to do physical activity for minimum 30 minutes like brisk walk, riding a bike or lifting weights.
- Try to consume healthy, balanced diet dropping out the sugar and saturated fats.
- Quit smoking as it elevates the risk of diabetes and heart diseases.
Maintain a healthy weight and eat diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains and lean protein. Avoid sweetened drinks, processed foods. Consume suggested portion sizes.
Complications linked with Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic disease and harms organs and tissues of our bodies. High blood sugar comes along various complications:
- Heart ailments
- Neuropathy
- Nephropathy
- Retinopathy
- Hearing loss
- Foot injury that doesn’t heal
- Bacterial and fungal skin infections
- Depression
- dementia
Conclusion
Generally Diabetes symptoms are not visible enough to identify it. It is necessary to rush to your doctor in case you are experiencing any symptoms mentioned above. Early detection can prevent or delay diabetes.