Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
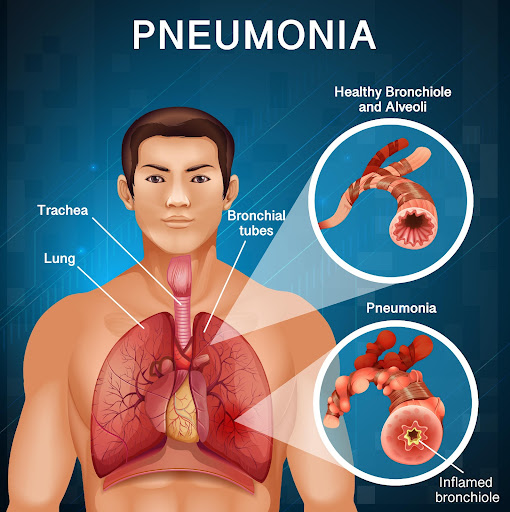
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a bacterial, viral or fungal infection in one or both the lungs. Pneumonia in both of your lungs is called bilateral or double pneumonia. The air sacs of the lungs are filled up with pus or fluid, leading to cough with phlegm, fever, chills and irregular breathing. The infection causes inflammation in the air sacs which is called alveoli.
Pneumonia varies from mild to acute. Children, infants, people over 65 years of age and people with feeble immune system are at a greater risk of Pneumonia.
Bacterial pneumonia is more intense than viral pneumonia, which clears up on its own.
You can get Bacterial and viral pneumonia:
- From person to person through sneeze or cough.
- By being in contact with surfaces or things that are contaminated with viral or bacterial pneumonia.
- You can get fungal pneumonia from the environment.
How is pneumonia acquired?
- Hospital acquired pneumonia: it is an acute bacterial pneumonia which you can get during your stay at a hospital.
- Community acquired pneumonia: you get this outside an institutional and medical setting.
- Ventilator associated pneumonia: when you use a ventilator you get pneumonia and is called VAP.
- Aspiration pneumonia: is caused when you inhale some bacteria into your lungs via food, drink or saliva. Chances of getting it are relatively high if you have swallowing issues or if you are tranquilized from the use of certain medicines, alcohol or drugs.
Stages of Pneumonia:
Stages of pneumonia depend on the affected areas of the lungs:
Bronchopneumonia: can harm the areas of both the lungs. It is confined adjacent to or around your bronchi. These tubes lead from your windpipe to your lungs.
Lobar pneumonia: impacts one or more lobes of your lungs. Each lung is made of lobes, which are specific sections of the lung. On the basis of how it progresses, lobar pneumonia is categorized into four stages:
- Congestion: Lung tissues seem to be heavy and congested. Air sacs are filled with infectious organisms.
- Red hepatization: Lungs look red and rigid because Red blood cells and immune cells have plunged into the fluid.
- Gray hepatization: Red blood cells collapse while immune cells survive. The collapse in red blood cells leads to the change in colour, from red to gray.
- Resolution: immune cells begin to get rid of the infection. A productive cough expels the rest of the fluid from the lungs.
Causes of pneumonia:
Various germs can be the reason of pneumonia especially the bacteria and viruses present in the air we breathe in. Generally our body fends off these germs from infecting our lungs but sometimes these germs can suppress your immune system.
Pneumonia happens when germs cause an infection by entering your lungs. The immune system’s response to void the infection can lead to the inflammation of air sacs (alveoli). This ultimately causes the air sacs to fill up with pus and liquids, causing pneumonia symptoms.
Bacteria can be the reason in adults and viruses are the most typical cause in school-aged children. Some illnesses that cause pneumonia are:
- Rhinovirus
- COVID-19
- Influenza virus
- HMPV
- HPIV
- Legionnaires’ disease
- Mycoplasma pneumonia bacteria
- Pneumococcal disease
- Pneumocystis pneumonia
- RSV
Symptoms of pneumonia:
Symptoms and indications of pneumonia rely on its causes. Symptoms can vary from mild to acute. Everyone experiences different symptoms.
Bacterial pneumonia symptoms:
can occur instantly or gradually. Some of the symptoms are:
- High fever up to 105 F
- Yellow or bloody mucus cough
- Fatigue
- Fast breathing
- Irregular breathing
- Abrupt heart rate
- Chills or sweating
- Pain in chest and abdomen while coughing or deep breathing
- Poor appetite
- Cyanosis
- Confused state of mind
Viral pneumonia symptoms:
Generally take various days. Symptoms might be similar to bacterial pneumonia along with the other symptoms:
- Dry cough
- Headache
- Stressed muscles
- Fatigue
Symptoms of Pneumonia in kids:
Sometimes symptoms of Pneumonia in kids and newborns are not visible and may differ from adults. Some of the symptoms are:
- Fever and chills
- Sweating
- Cough
- Rapid breathing
- Poor appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Being energy less
- Restlessness
Certain indications in babies and children are:
- Groaning sound with breathing
- Less pee
- Pale skin
- Limpness
- Crying more than normal
- Issues in feeding
Symptoms of pneumonia in adults
Adults over 65 or those with feeble immune systems display mild symptoms of pneumonia. These symptoms worsen with the passage of time. Adults may experience:
- Abrupt mental change
- Low appetite
- Fatigue and tiredness
Prevention:
The best way to evade pneumonia is to get vaccinated against the bacteria and viruses that are generally responsible for it. One should take some necessary precautions to lower the risk of pneumonia. Certain lifestyle changes can also show some positive results.