Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
What is Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
It is a chronic, inflammatory disease that can harm more than just your joints. It occurs in the joints on both sides of the body, it means that if joint of one arm or leg is damaged, the very same joint in the other arm or leg will be affected, too. This disorder can harm various body systems, such as the eyes, lungs, heart, skin and blood vessels.
It is an autoimmune disorder, which means it accidentally strikes your own body’s tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis potentially influences the joints lining, causing a painful inflammation that can lead to the decaying of the bones and joint deformity. The swelling caused by rheumatoid arthritis can harm the other parts of the body. Acute rheumatoid arthritis can cause physical disorders.
Unchecked swelling harms the cartilage, which generally acts as a “shock absorber” for your joints. With the passage of time this can deform your joints. Ultimately, your bone deteriorates itself. This can result in the fusion of your joints. Certain cells in our immune system support this process. These substances are created in your joints but also flow and cause symptoms throughout your body.
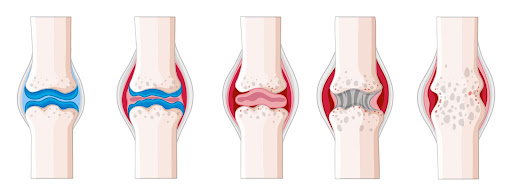
Stages of Rheumatoid arthritis:
There are 4 stages of RA:
- Stage 1: In the beginning, joints tissue is inflamed. In the X-rays you can’t see the deterioration of the bones. You may experience discomforting pain.
- Stage 2: the swelling harms the cartilage in your joints which can compromise your mobility causing stiffness.
- Stage 3: the swelling is so intense that it harms your bones. You will experience discomfort and stiffness, resulting in physical changes.
- Stage 4: your joints keep deteriorating and the swelling stops, making you immobile and stiff.
Causes of Rheumatoid arthritis:
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. Generally, our immune system shields our body from various infections and diseases. In this our immune system harms healthy tissues of our joints, making the lining cells to divide and lead to swelling. Chemicals are released during this process that can harm bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments. If left untreated the joint will become weak and deform. It can lead to medical issues linked to our heart, lungs, nerves, eyes and skin. The cause of rheumatoid arthritis is still unknown. Researchers believe that it’s caused by a fusion of genetics, hormones and environmental factors. Certain infection, smoking, physical or emotional stress may trigger it.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid arthritis:
RA impacts everyone in a different manner. In some people symptoms may develop over the years and in some people symptoms may appear promptly. The symptoms may differ in intensity and may appear or disappear.
Early RA initially, impacts your smaller joints – probably the joints that fasten your fingers to your hands and your toes to your feet. As the disease proceeds, advance to the wrists, knees, ankles, elbows, hips and shoulders. Mostly symptoms appear in the same joints on both sides of the body.
RA causes inflammation and agony in joints. These symptoms aggravate during periods known as flares or exacerbations.
Generally RA symptoms harm the hands, knees and wrists joints but can cause a great impact on the tissues and organs of the body such as lungs, heart and eyes. Approximately 40% people with rheumatoid arthritis don’t experience any symptoms or indications. Some of the affected areas are:
- Eyes
- Skin
- Lungs
- Heart
- Kidneys
- Salivary glands
- Nerve tissue
- Bone marrow
- Blood vessels
Some of the known RA symptoms are:
- Vulnerable, warm, swollen joints
- Fatigue, fever and poor appetite
- Pain or swelling in more than one joint
- Joint stiffness which is more painful in the morning or after being inactive
- Experiencing the same joint symptoms on both sides
- Joint deformities and deterioration
- Fever
Never ignore the symptoms; early detection will help in the treatment.
Rheumatoid arthritis risk factors:
Mentioned below are the risk factors that lead to rheumatoid arthritis:
- Family history: if any of your family members has RA, you are more likely to have this disease.
- Gender: women have more chances to develop RA than men.
- Smoking: smoking alleviates the risks of rheumatoid arthritis and makes it worse.
- Obesity: obesity leads to rheumatoid arthritis.
- Age: RA can develop at any age but generally it develops in the middle age.
- Genes: people born with genes called HLA class II genotypes have more chances to develop RA. The chances double in people who are obese and are open to environmental factors.
- Live birth history: people who have never given birth are more prone to develop RA than those who have given birth.
- Exposure to environmental factors: according to a trusted source smoking mothers children are at greater risk of developing RA as adults.
Takeaway:
RA is an acute incurable disease. It has no persistent symptoms. RA differs from person to person and symptoms ranging from mild to stern. In RA joints will get worse with the passage of time, which is why it is imperative to seek proper treatment to evade any serious joint injury. Immediately consult your health care provider if you come across any symptoms.