Disclaimer:
This article is for information purposes only. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Seek medical care for your treatment.
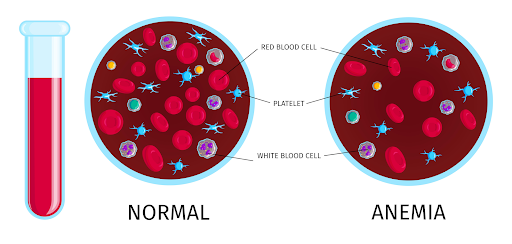
What is Anemia?
Anemia is a condition in which you don’t have sufficient red blood cells to carry ample oxygen to the tissues of your body. Red blood cells in our body carry oxygen throughout our body. Oxygen strengthens our cells and gives us the energy. Anemia can be mentioned as low Hemoglobin and can make you feel fatigued and worn out.
There are various forms of anemia, each with its own reasons. It can be short-lived or permanent and can vary from mild to acute. Generally, anemia has various causes. Treatment of anemia depends on its cause and can be treated by taking medicines or by following proper medical procedure. Avoiding anemia symptoms and its treatment can be destructive for your health. In U.S. anemia is the recurrent blood condition. It influences virtually 6% of the population. People with prolonged ailments, children and women are more prone to have anemia.
Function of Red blood cells
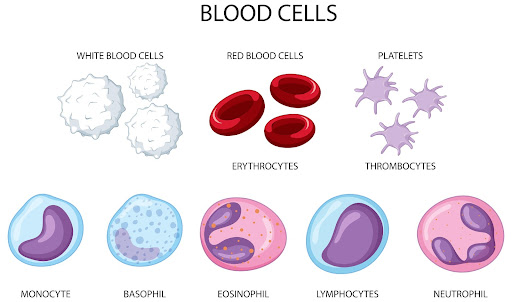
Most of the blood cells are created in our bone marrow. There are three types of blood cells that our body makes.
- White blood cells to combat infections
- Platelets to clot our blood
- Red blood cells to take oxygen from our lungs to the rest of the body and carbon dioxide back to lungs from the body.
Types of Anemia:
There are probably more than 400 types of anemia and they are divided into 3 significant groups:
- Anemia caused by excessive blood loss.
- Anemia caused by defected red blood cells production.
- Anemia caused by the demolition of red blood cells.
Causes of Anemia:
According to ASH, lack of iron is the chief cause of anemia. Different types of anemia have various causes:
- Inadequate iron anemia:
This happens because of lack of iron in our body. Bone marrow makes iron with the help of hemoglobin. Iron deficiency fails our body to produce required hemoglobin for red blood cells. Pregnant women suffer from this type of anemia without any iron supplementation. Excessive blood loss can also be the reason of it, such as menstrual bleeding, stomach or bowel ulcer, cancer of large intestine. Sometimes use of some non-prescribed painkillers like, aspirin, can create swelling of the stomach lining resulting in blood loss. It is imperative to establish the reason of iron deficiency to avert anemia and its recurrence. Consuming insufficient iron for a long time results in the lack of iron. Foods like eggs, meat and green leafy vegetables are rich in iron. Iron plays a crucial part in development and growth which is why it is suggested for pregnant women and growing kids.
- Vitamin deficiency anemia:
Lack of vitamin12 and folate can cause vitamin deficiency anemia. Your body needs these two to make healthy red blood cells. Absence of these or other chief nutrients hamper the red blood cells production. When some people consume B-12 in abundance they are not able to absorb the vitamin which leads to vitamin deficiency anemia called as anemia. Certain medicines, alcohol misuse and intestinal diseases can contribute to vitamin deficiency.
- Anemia of inflammation:
Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, kidney ailment, Crohn’s disease, cancer, HIV and other critical inflammatory diseases can intervene in the production of red blood cells.
- Aplastic anemia:

This is lethal anemia and happens when your body fails to produce required red blood cells. There are various causes of aplastic anemia such as infections, medication, auto immune diseases, radiation, chemotherapy, genes or infection.
- Anemias associated with bone marrow disease:
Diseases like leukemia and myelofibrosis can cause anemia by impacting blood production in bone marrow. The influence of these cancerous disorders can be life risking.
- Hemolytic anemias:
It is a disorder when red blood cells die faster than bone marrow can replace them with new blood cells. Some blood diseases elevate red blood cells destruction. Genes, some medications and infections are the causes of hemolytic anemia.
- Sickle cell anemia:
This inherited, critical condition is caused by shoddy form of hemoglobin that persuades red blood cells to presume an abnormal sickle shape. These uneven blood cells die untimely, leading to the deficiency of red blood cells.
- Blood loss during pregnancy or menses:
Pregnancy and excessive menstrual bleeding leads to iron deficiency. During pregnancy our body needs more iron to create sufficient oxygen for the baby.
- Internal bleeding:
Some medical conditions like stomach ulcer, polyps in intestines or colon cancer can cause internal bleeding leading to anemia.
- Inefficacy to absorb iron:
Some surgeries or diseases that distress the intestines can intervene with how your body absorbs iron.
- Endometriosis
It is hard to diagnose if you have endometriosis. You may have excessive blood loss during periods if you have endometriosis.
- Genetics:
Celiac disease makes it hard to absorb iron and is often passed down through families. Other genetic conditions also lead to anemia.
Symptoms of anemia:
Sometimes it is hard to determine anemia but with the passage of time symptoms of anemia become visible.
- Tiredness
- Fatigue
- Pale skin
- Irregular breathing
- rapid heartbeat
- Lightheadedness
- Pain in chest, bones and joints
- Growth problems in teens and children
- Pounding sound in one of your ears that may come and go
- Tingling sensation in legs
Prevention:
We can avert anemia by consuming minerals, folate, vitamin and iron rich diet.
Conclusion:
Iron is a significant nutrient for our body. Anemia is the result of lack of red blood cells or if the red blood cells are not working properly. Some people are born with anemia but many develop with the passage of time. Immediately consult your doctor if you experience any anemia symptoms.